Glossary
A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z
A
Account – An Out of Home advertiser or agency.
Account Executive – The primary user who is the contact for this account.
Advertiser – The seller of brands. Advertisers may be represented by agencies.
Ad Serving – Broadsign Ayuda supports four different ad serving methods for use in different circumstances. These can often be used together.
- Bumpable booked spots – Replacing bumpable booked spots with ad server content can optimize bumpable Booked Spots revenue.
- Unsold time – Ad server content can be sought when a loop is not filled completely. This is configured in the loop template.
- Reserved loop time – Time for ad serving can be reserved in loop templates.
- Specific VAST designs must be shown – Specific VAST advertising, filler, or editorial content, can be presented. VAST settings in the player configurations are the baseline. VAST settings for designs take priority only when these need to be distinct from the overall player configuration settings. To put this another way, players prioritize the design VAST URL over the VAST URL for unsold time.
Note: Unsold time can be differentiated between time with or without filler.
Agency – firm that creates and is responsible for overall planning and of the advertising campaign. It may also be responsible for marketing and promotion.
Alto – Alto is a Broadsign Ayuda web application for your customers so they can upload, organize and schedule designs to their campaigns.
Assets – The stock of available billboards and digital signage.
Attributes – Attributes are additional customer specific labels. For example, portrait or landscape may be configured as attributes. Demographic breakdowns may be another attribute. Attributes can then be used as filters, restrictions or sorts.
Avail – The status of inventory, that is, is it available? An avails package is a report built in Juice to inform the buyer what faces might be purchased.
Availability Matrix – Each client can configure how availability is governed at their deployments. For example, what might have a status of maybe available might be configured as partially available at different customers. Only administrators can make changes to how availability works.
B
Bad Credit Status – This prevents users from creating proposals/contracts if the account is flagged with a bad credit status. Broadsign Ayuda also has an API so that external systems can be aware when this checkbox has been enabled.
Billboards
- 6 Sheet Billboards – 1.8 m x 1.2 m / 5.905 ft x 3.937 ft – Often used at bus stops, railway stations and shopping centres at eye-level.
- 16 Sheet Billboards – 3.048 m x 2.032 m / 10 ft x 6.6 ft. Typically find 16-sheet billboards in highly urbanised areas that boast significant traffic.
- 32 Sheet Billboards – 3.048 m x 4.064 m / 10 ft x 13.3 ft – These adverts tend to be wider and may be encountered in locations where they are visible from some distance.
- 48 Sheet Billboards – 3.048 m x 6.096 m 10 ft x 20 ft – 48-sheet adverts (whether they are landscape or portrait in their design) are the single most popular. Traditional 48-sheet billboards are often installed at the side of busy roads, particularly A-roads or those that lead towards major cities or shopping centres.
- 96 Sheet Billboards – 3 m x 12 m / 9.842 ft x 39.37 ft – The largest standard advertising type combines two, 48-sheets side by side. These towering adverts are also likely to be found at roadsides, particularly prominent motorways, junctions and commuter transportation.
Billing Schedule – A billing schedule is used to organize billable items into invoices according to a schedule. Each campaign must choose at least one. A billing schedule template is the leader for those billing schedules. Users may also encounter the term invoice schedule. This is a synonym for Billing Schedule. Typical billing schedules are:
- Once at the beginning – Creates one invoice for the period of the campaign that contains all the segments and faces.
- Lunar – Creates the invoices with 28-day periods. Calculates the media amounts pro-rated, as per the number of days in the scheduled invoice.
- Monthly – Calculates the media amounts on a pro-rated month per month basis, as per the number of days in the scheduled month.
- MonthlyFixed – Each invoice will have the same amount per face/segment, per invoice without taking into consideration how many scheduled days in the month. For example, if there's a campaign with one face from the beginning of February to the end of March, the amount for each invoice will be the campaign amount divided by two. If the face is only partially in an invoice, it will be pro-rated based on the number of days it is contained in the invoice.
- Quarterly – Creates the invoices with three-month periods. Calculates the media amounts pro-rated, as per the number of days in the scheduled invoice.
Bill Poster – The individual tasked with installing static copy. Bill Posters report to the Operations Manager.
Blueprints – Outdoor media maps are typically created using external geo-location services. Indoor media can use blueprints that are uploaded and have inventory markers placed on them.
BMS – You may see references to BMS on some Broadsign Ayuda screens. BMS is the underlying toolset used to deploy Broadsign Ayuda at customers. Generally, only administrators and finance users need access to it.
Bonuses – The manual allocation of inventory to make up for shortfalls in performance. Large campaigns may have a ‘safety margin’ of a bonus segment to account for content that should have been scheduled but was not, or to account for other delivery problems such as the unavailability of busses, vandalism, repairs or construction.
Bonuses can be mandatory and built into the contracts for large accounts. Bonuses can also be optional or ‘good will’ actions. Regardless these are all manually scheduled and are not automatic overflow calculations in Broadsign Ayuda.
- Guaranteed Bonus – This status will be used when space is to be delivered to an advertiser at no extra charge.
- Non-Guaranteed Bonus – This status is used when space is to be delivered, only if available, at no extra charge.
Do not confuse with moveable and pre-emptable (see Fixed).
Booking – Booking and scheduling do not refer to the same thing. A booking is the reservation of a face. Scheduling is when the design is to be displayed.
Booking Types – There are terms dictating how flexible purchases can be.
Brand – Brands are not an informational item in Broadsign Ayuda. Campaigns are. Advertisers are. However, it is the advertiser who needs to track their brands, not the owners of digital or static signage.
Bundle – A collection of designs similar to a file folder or directory. Bundles are used primarily in digital scheduling. Media bundles cannot contain other media bundles. Designs can appear in multiple media bundles.
There are special use bundles for fail overs and special circumstances (see Unsynchronized Bundle).
C
Calendars – Calendars are encountered in invoicing. Billing calendars use the twelve calendar months.
- Billing calendars start on the first of the month in which the relevant segment starts.
- These ends on the last day of the month in which the relevant segment ends.
Broadcast calendars are usually based on the lunar calendar, which is four weeks to a month for a total of thirteen months.
- Broadcast calendars always start on a Monday and end on a Sunday.
- These use the first day of the Period Start Date.
Campaign – The contracted purchase of faces to display designs for specific date ranges. In practical terms, a campaign can be thought of as a group of segments.
Category – A broad label to add detail to advertisers, agencies, sites and media. For example apparel, retail or insurance. Site categories may be digital, static or transit. Do not confuse these types of with the Separations Category. Those exist to prevent similar ads from running next to each other. Categories are very general.
Cerebro – Cerebro™ is a non-linear, mathematical optimization engine that uses meta-heuristic numerical techniques to reproduce the decisions made by skilled media planners. Cerebro is a set of APIs-as-a-service for software developers at OOH companies. It helps developers build programs that can generate optimized media plans and proposals that include TAB OOH Ratings or Route UK data into their custom software.
Channel – Channels are a method of loop customization giving digital schedulers more granular control over how content plays. Channels can group specific types of content, and that content can be sourced from different bundles.
Chartist – The person responsible for converting the contract into an actionable campaign, right down to the level of the individual face. This is an older term in the advertising world that comes from the paper days when they would literally be looking things up on charts.
The term chartist is not used universally. However, for clarity in Broadsign Ayuda documentation, we use Chartist to mean someone working on static campaigns and Digital Scheduler to mean someone working on digital campaigns.
Check-in interval – The frequency at which the player connects to seek updates.
Configuration Model – The Player Configuration settings appling to specific players.
Contact – An external user. For example, an agency. Another example might a contact with permission to use Alto, the Broadsign Ayuda OOH software product that allows your customers to upload content to your team.
CPM – Cost per thousand (CPM) is a marketing term used to denote the price of one thousand advertisement impressions. The M refers to the Roman numeral for one thousand, mille (pronounced as in 'fill').
Contract Status – The lifecycle stage of the agreement between the asset owners and the purchaser
- Pending – Used to define a contract that is still awaiting a final approval or has not been received.
- Contracted – Used to define contracts that have been approved.
- Limited Hold – Used for a possible contract that may need faces for a specific period. When selecting this option the expiry date will need to be seen as well. This does not actually reserve the faces.
- Unlimited Hold – Used for a possible contract that may need faces for an unlimited time period. This does not actually reserve the faces.
Copy – Printed materials to be installed on static faces such as billboards, street furniture or vehicles.
Copy Change – Copy changes are used to replace one static design with another for the same booking.
- Replacing a coming soon teaser ad with the campaign's main ad. Typical examples include:
- An emergency copy change to replace a design that has incorrect artwork or spelling.
A much rarer use for the copy change feature is that the facility is inaccessible, or crews are unavailable on the date a campaign starts. A temporary design is posted first with the intention to replace it with the correct design later.
Similar sounding features include filler and cover posters. Filler copy can be posted to cover the face if replacement copy is not immediately available. Cover posters may be required in the event of damage, vandalization or theft.
Copy Restrictions – User-defined Copy Restrictions that can be assigned to Faces. For example, tobacco advertising might not be accepted by sports facilities or alcohol ads may not be allowed near schools.
Cover Posters – Cover posters may be required in the event of damage, vandalization or theft. See also Copy Change and Filler.
D
Dayparts – The time of day for a digital face. Many companies use a single daypart for the entire day but others may have dayparts for rush hour, or evenings, weekends or other periods.
Design – The creative material to be shown on faces.
Design Variants – Design variation codes are a marker that two or more designs can share so that one design can be substituted for another sharing the same variation code. This feature is often used with Sync Groups to swap out a single design for one face even though these faces are being administered by the same loop.
| Face 1 | Face 2 | Face 3 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Booking Line 1 | Design 1 | Design 1 | Design 1 |
| Booking Line 2 | Design 2 | Design 2a | Design 2 |
Daily Effective Circulation (DEC) – Daily Effective Circulation is the average number of passers-by in cars or other vehicles, that could potentially be exposed to an advertising display or billboard for either 12 hours (non-illuminated – 6:00 am to 6:00 pm) or 18 hours (illuminated – 6:00 am to 12:00 midnight) on an average day. Many billboard operators use actual traffic counts provided by departments of transportation to make these calculations.
Debtor Code – This is used to direct incoming monies to a specific account.
Digital – Broadly, an electronic ad or campaign. How does digital differ from static? At the risk of stating the obvious, digital signage can support a collection of ads that cycle in loops. These are called spots and spots can have different lengths and frequencies in a loop. See Saturation.
Digital Scheduler – See Chartist.
Digital Signage – Digital signage is a subset of signage. Digital signs use technologies such as LCD, LED and projection to display advertising.
Direction – The compass orientation to which a face displays.
Dirty – Invoices that have been changed have their approvals removed automatically. These invoices require re-approval. (The term 'dirty' does not appear in the Broadsign Ayuda user interface.)
Division – A subset of a company. For example, digital and static may be two divisions. Or a company with different legal entities in different countries may have divisions for each state. The practical effect is that campaigns may be run by one division but billed to a parent firm or sister division.
Download Days – How many days of schedule the player should download ahead of time. If the player fails to connect to the Cloud and its schedule comes to expire, it will keep going with the last schedule it had.
Download Hours – Periods during which the Splash Player is allowed to download media files. By default, there are no restrictions.
DPOP – Digital Proof of Play.
Dynamic Content – Digital designs can be enriched with dynamic content. For example, a lottery advertisement may present last week's winning numbers and the value of this week's prize. There are several kinds of dynamic content:
| External Dynamic Content | Built-in Dynamic Content |
|---|---|
| Content from a web page | Current date and time |
| Dynamic Linking to Content from XML | Countdown |
| Externally hosted images | QR Codes |
| Forward and Store | |
| Forward and Play |
These features can work together. For example, the link to an external image may provide the background to content that is sourced from a web page, and then has a countdown timer indicating how many days to an event.
E
Emergency Message – A special form of digital scheduling that immediately overrides content. It is used to communicate important information such as evacuation instructions, amber alerts or weather warnings.
Extension – Some billboards can have extensions put on them. An example might be an arrow extending from the sign.
F
Face – The advertising surface. For example, a billboard may have one face. If the billboard has rotating images there may be three faces. A digital sign's face may have multiple zones or virtual faces to play different content top and bottom, or left and right.
Face is one of two mandatory hierarchy levels for assets (see Sites and Hierarchy). Faces can be grouped into Packs for convenience.
Filler – A digital content type that will play if no advertising content or editorial content is available for a loop spot. Their purpose is to prevent blank screens (see also Restrictions). In static campaigns these may be referred to as house ads (see also Copy Change and Cover Posters).
Fixed – The location is guaranteed to the advertiser. The location has been sold and it cannot be moved or pre-empted or changed. Generally, most purchases are fixed. Do not confuse this with the other uses of the word filler in Broadsign Ayuda. Non-fixed locations may be moveable or pre-emptable.
- Moveable – The face can be replaced by another location of equal value during the campaign
- Pre-emptable – The face can be removed from the campaign with no guarantee of a replacement
Do not confuse moveable and pre-emptable with guaranteed and non-guaranteed.
Floating content – What some Broadsign Ayuda customers call unscheduled content. Broadsign Ayuda refers to two types of floating content, filler and editorial.
Forward and Play/Store – This allows designs to be linked to sources available via FTP. Forward and store downloads all of the content in the entered directory to the player for display. Forward and play downloads only the latest version of the specified file from the target directory.
Frequency Capping – Restricting (capping) the times (frequency) a specific visitor to a website is shown a particular advertisement. This restriction is applied to all digital media serving ads from the same advertising network.
G
Gross Rating Point (GRP) – A measure of expected ad performance in relation to the number of people in the target for an advertising campaign. GRP is commonly used by media buyers to compare the advertising strength of components within a media plan. If a billboard campaign has an average rating of seven, and an ad is placed on five billboards, then the campaign has 7 × 5 = 35 GRPs. GRPs can also be related to measures of the reception of the ad campaign. If an ad campaign results in 50% of the target seeing the advertising three times on average, then the campaign's size was 150 GRPs: GRPs (%) = 100 * Reach (%) × Average frequency (#).
Group Scheduler – This allows chartists and digital schedulers to apply bundles to bookings by creating groups/ and filters based on dates, spot length, network, media, areas, time, faces and inventory attributes.
H
Hierarchy – The Broadsign Ayuda Platform supports up to five levels in the Asset Hierarchy:
- Sites
- Vehicles
- Locations
- Frames
- Faces and inside faces, zones.
There are two mandatory levels at all times: Site and face: each face must be inside a site and sites must contain at least one face. These hierarchy levels can contain many customizable attributes that differ from company to company.
I
Impression – An interaction with a piece of content with an audience member
Inactivity – There are three fields for inactivity: Inactivity Planning End Date, Expected and Actual Planning End Date is purely informational and has no impact on availability. Planning end date is a note for when your team plans to have the Face saleable again.
- Planning – Future date which does not affect avails
- Expected – Future date which does affect avails
- Actual – Availability date which does affect avails. Users cannot enter actuals that are in the future.
Inventory – A synonym for assets (see Hierarchy, Site, and Face).
Invoices – A flat invoice is the file after transferring a batch. A non-flat invoice is the report created when printing an invoice.
Invoicing Schedule – See Billing Schedule.
J
Juice – The product suite used by sales users and sales managers to create proposals (see Splash).
L
Leader and Follower Players – This self-adjusting group is used to overcome network timing issues. A Sync Group requires a Leader player and at least one follower. Players in sync groups elect leaders on their own. Every five seconds, the Leader broadcasts a heartbeat to signal its existence. If a follower goes more than ten seconds without hearing from its Leader, it will switch to being a Leader itself and start broadcasting both orders and a heartbeat.
Limited Hold – Proposals by default do not hold inventory. Inventory in proposals is still considered available and can be made use of by other campaigns at any time. However, sales users may reserve inventory for small amounts of time during the sales process. This is so clients have time to review the proposals. Proposals with a limited hold status show up in the timeline view with a status of Maybe Available (see Availability Matrix).
A similar sounding feature is Proposal Valid Until.
- Limited holds are meant to have an impact on inventory. Holds are for when the contract is highly likely and there is a need to reserve inventory.
- Proposal valid until is more that you have created a proposal, there is an expiration date on the price and inventory.
Limited Holds also differ in that they represent a campaign status. Proposal Valid Until is merely a date field in a proposal.
Linked Users – Users in the same department can be linked in the user records so that they can share information. A typical use case might be an Operations Manager will be linked to all of the bill posters. This will allow the operations manager to see the work orders that have been assigned to them. The team grouping is largely used by sales users. It is most visible in reporting on team activities (see also Roles and Types).
Loops and Spots – A loop is a container for multiple digital ads known as spots. Loops are part of the inventory and controlled by your system administrator. Different loop templates may be configured to run at different dayparts. Consequently, when the digital scheduler includes an ad a particular time of day, the correct loop template is chosen automatically.
The closest to an industry standard loop is a 64-second loop made up of eight-second spots. Other common loops are:
- 180:10
- 90:15
- 80: 10
Loops are important properties for a company's inventory and most users to not have the ability to edit loops since it would change the value of the inventory.
Lunar calendar – A four-week calendar. It is sometimes called a 28-day calendar (see National/Local).
M
Media – The specific type of static or digital media such as poster, or bus shelter, et cetera.
Media Frame Synchronization – See Player Synchronization.
Mimic this Player – Allows one player to act as a clone of another. Mimic players are useful for in-loop debugging, testing, in-office monitoring of remote or difficult to access faces. Mimics do not contribute to Proof of Play statistics.
MRAID – Mobile Rich Media Ad Interface Definitions is a specification released by the Interactive Advertising Bureau (IAB) that sets a common API for mobile rich media ads that running in mobile applications.
N
National / Local – National ads book in weeks. Local ads typically book in months.
Network – Networks are themed groupings of sites. Unlike packs which are purchasable groups of sites, networks are not purchasable as a group but are used to indicate broad categories such as street furniture, vehicles or cinemas.
O
Office – Each Broadsign Ayuda deployment must have at least one office configured. That office must link to at least one sales market. Office types include:
- Headquarters
- Payment
- Remit
Out of Home (OOH) – Out of Home advertising is advertising that reaches consumers when they are outside of their homes. It is distinct from print, radio, television or mobile advertising. The most traditional form of OOH advertising is the static billboard. The advent of mobile digital billboards and their enhanced capabilities are adding the benefits of OOH. (See the Wikipedia entry on OOH.)
Operations – The department tasked with installing physical ad copy onto billboards, pillars, furniture and other physical locations. The operations manager uses work orders to issue instructions to bill posters.
Order – The order of faces at a site. This legacy feature is replaced by position.
Other Costs – This is a synonym for Additional Revenues. Both terms are used in the product.
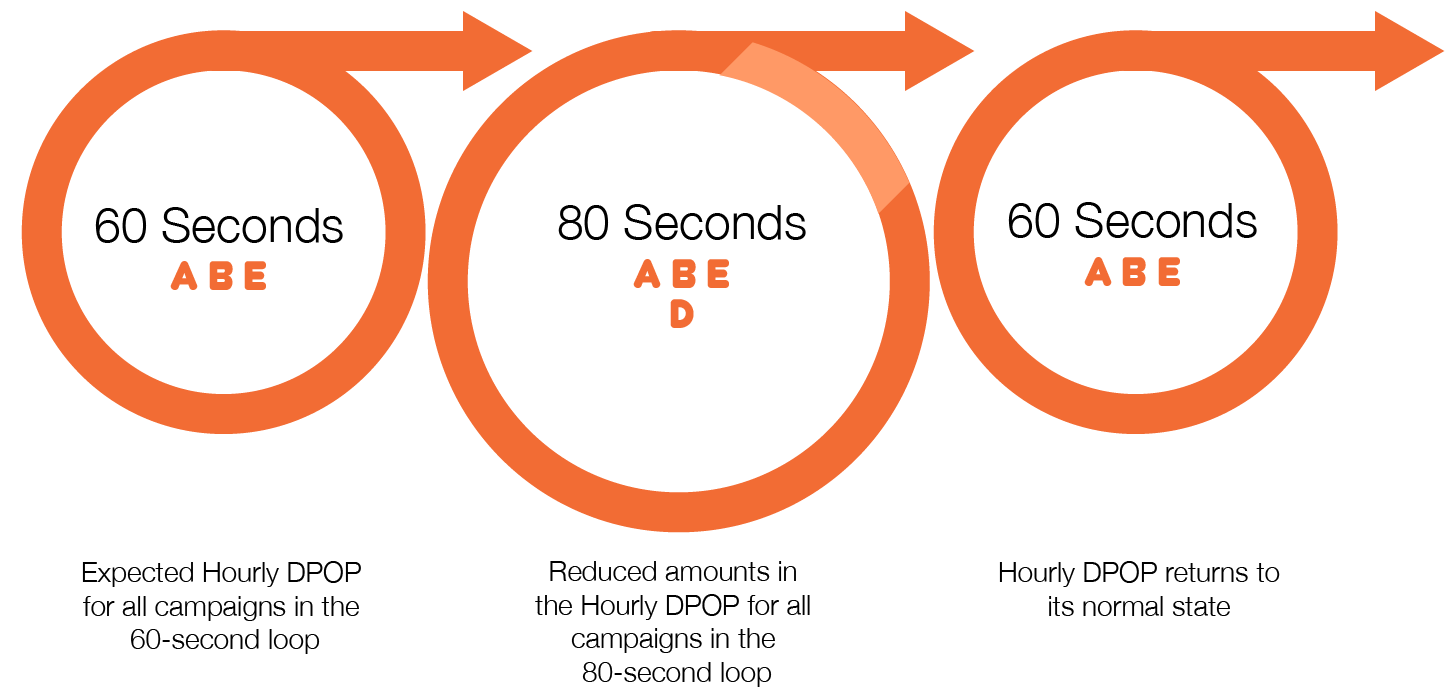
Overbooking – Overbooking will allow you to include additional campaigns inside a loop that has already reached its total capacity. The consequence of this will be a longer loop and therefore fewer loops played during the overbooking.
There is a campaign with faces A, B, C, D and E. Our loop has 60 seconds. Faces A, B and E are available. These are booked as usual. C is not available and D is partially available. The loop has an empty spot.
The system adds the campaign to the loop to take advantage of this unused time.
If the digital scheduler includes a new overbooked campaign for 20 seconds more, the platform will make a temporary enlargement of the loop from 60 seconds to 80 seconds. It is important to note that this reduces the amounts in the Hourly DPOP for all the campaigns in the loop, not merely the overbooked campaign.
Digital overbooking does not factor in non-guaranteed statuses or any other factors.
P
Packs – Packs are groups of faces.
- Transparent – The default is that users can drill into packs and see all of their faces.
- Non-Transparent – Some packs are not transparent. Users are not able to identify their faces.
- Breakable – Breakable packs can have individual faces booked.
- Non-Breakable – Packs that cannot have individual faces booked are called non-breakable
- Pack of Packs – Broadsign Ayuda clients with very large collections of assets may use nested packs.
Face packs have only single sales markets. Face packs must link to segments, which support only single sales markets.
Face packs can be organized in hierarchies so that different rate cards can apply at different levels. The lower levels inherit the rate cards of the upper levels unless another rate card is assigned.
Photo Sheets – These contain face-level information and images of faces.
Plant – A physical location for managing printed media.
- Posting Plants – Where the Bill Posters obtain the copy for posting.
- Order Plants – Where posters get delivered.
Player Synchronization – This ensures multiple players start playing the same media file at the same time.
Play Log – Data created by a player of activity. It is used to prove that a given design has played.
POI – Point of Interest.
POP – Proof of Performance.
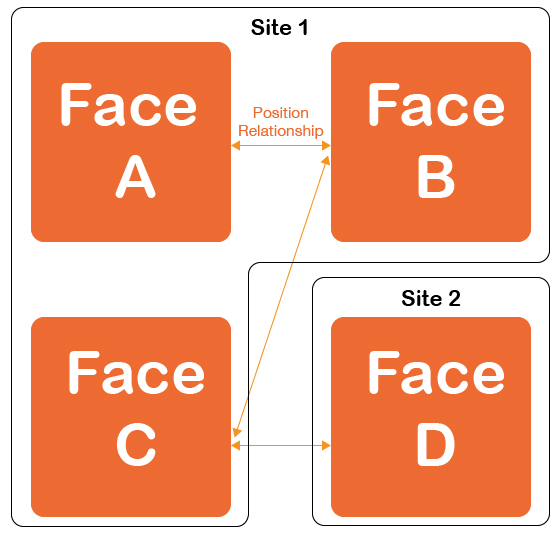
Position – The geographic relationship between faces. Having the geographic position of each face relative to every other face prevents competing ads from accidentally running within line of sight of each other. Do not confuse Position with Relationship, Site or Direction.
Posting – A design linked to a face booking.
Programmatic Ad Serving – Broadsign Ayuda supports programmatic ad sales but the feature is called ad serving. Advertisers use Agencies and Demand Side Platforms or Networks to buy media through Exchanges and Supply Side Services such as Broadsign Reach (see also Ad Serving).
- Sell Side Provider (SSP) and Demand Side Platform (DSP) – Think of these as the loading dock and storefront, respectively. These are two sides of the same coin. The Sell Side Server is what connects OOH inventory managed by Broadsign Ayuda to the outside world. The DSP is what buyers use to locate and purchase inventory.
- Agency Trading Desk (ATD) – Groups within agencies that have built, acquired or licensed DSP services. Trading desks source advertising inventory for the ultimate clients.
- Data Management Platform (DMP) – A platform allowing agencies and advertisers the ability to manage and make better use of their first and third party data. Often integrated with ad servers and DSPs to enable easy access and use.
Priority Filler Percentage – Some filler designs can be assigned as higher priority fillers. The player will try to keep the percentage of high priority fillers played above this number.
R
Rate Card – Rate cards are where the prices of faces are entered. This is generally the maximum price but typically advertising buyers will pay less than this as they negotiate for rates, and the sales team offers incentives.
Many rate card types can be configured and active at the same time. However, each face can have only one rate card active at once in a campaign. (Rate cards for additional revenues, fees, fines and services are separate.) Also, rate cards must be unique: Broadsign Ayuda prevents users from creating rate cards that have the same characteristics.
- Flat Rate Cards – Flat rates are constant prices. These will be used in most cases.
- CPM Rate Cards – CPM Based rates allow users to enter prices that are multiplied against the values contained in the Audience cards. Cost per thousand (CPM) is a marketing term used to denote the price of one thousand advertisement impressions.
- Audience-Based Rate Cards – Impressions and demographics are used to value the face. These cards only indicate the demographics not the price. The Audience card is calculated against the CPM card to arrive at a price. Audience cards are not used by themselves.
- Additional Revenue Rate Cards – Rates for content creation, production, installation, fines and fees.
Note: It is not possible to link an audience card to a CPM card directly. Faces are what connect audience and CPM cards. (Logically it can work no other way since there is nothing to charge for unless there's a face involved.)
Restrictions – These manage digital filler content. By default, designs marked as filler can play anywhere. Filler prevents black screens. Restrictions are used to control where specific filler items might show. An example might be that filler content for a shopping mall may be different from filler for digital billboards on the street.
Relationship – Face relationships refer to the parent/child relationship of virtual faces. Do not confuse this with Position, which refers to the geographic relationship between faces.
Revenue Types
- Scheduled – Revenues occurring in the ordinary course of events.
- Deferred – When revenue is recognized at a later date, meaning it doesn’t match the billing schedule dates.
- Accrued – When revenue is accumulated every week/month/quarter/year.
Ride – Attaching a later static booking to an earlier one because the booking or campaign has been extended. Rides essentially prevent unnecessary posting work orders from being issued.
Role – Roles determine what Broadsign Ayuda products and features the to which the user has access (see also Linked Users, Types).
S
Sales Market – Sales markets are groups of geographic areas. These reflect the sales and marketing strategies of each Broadsign Ayuda customer, and how they divide and report on their sales territories. Examples might be different areas in a city, Major markets, metropolitan, suburban, rural, highway, airports or schools.
Sales Restrictions – See Copy Restrictions.
Saturation – The number of times a spot appears in a single loop is called the saturation. Saturation does not apply to filler bundles.
Scheduler – See the Weekly Scheduler.
Scheduling – Scheduling and booking do not refer to the same thing. A booking is the reservation of a face. Scheduling is when the design is to be displayed.
Scheduling Groups – Scheduling groups is a tool for booking digital campaigns. It does this by means of an easy to use filter builder for creating schedules for segments, networks, media et cetera. A tremendous advantage of the group scheduler is that all the tools needed to create schedules – including a weekly scheduler – are in a single location. It reduces the need for complex arrangements of booking lines.
Screen – The video display unit attached to a player. Screens contain faces and it is the faces that display the content. Screens and faces are not synonyms. Why? Because screens can contain multiple zones / virtual faces.
Screen Multiplier – With some player configurations, the same image gets pushed to multiple screens from a single player. The screen multiplier is used to calculate proof of play. It does this by multiplying the plays against the number of screens.
Scroller – A type of static billboard that has posters on a roll. This roll cycles through a loop.
Segment – A subset of a campaign that has a date range, sales market and a media type. For example, the same ads running in bus shelters at the same date range in Manhattan and New Jersey would be different segments. Ultimately, a campaign can be thought of as a collection of segments.
Segments can be deleted up until action is taken on them.
- For static segments, this would be once postings are assigned.
- For digital segments, this would be once ads are played.
- If a segment is deleted by mistake, it cannot be undeleted. It must be re-created manually.
Separations Category – A feature in booking lines to keep ads from competing companies from running adjacent to one another. Do not confuse this with the general information Category field.
Sequence – A feature for organizing faces that has been deprecated (see Position).
Signed Date – This is the date that proposals are covered to the status of contacted. This date is entered automatically in the Basic Info screen of the campaign record.
Sites – Sites refers to the civic address where the media. Faces are the installation points at the site. Site is one of two mandatory hierarchy levels for assets (see Face and Hierarchy).
Snipe – A sticker applied to a billboard. These may be used to make corrections, change dates or to add new information without reprinting and reposting the entire billboard.
Splash – The product suite used by chartists and digital schedulers to execute campaigns (see Juice).
Splash Player – The devices controlling and displaying designs on digital signs. These can be fully fledged computers or purpose-built microcomputers optimized for presenting content on screens. Broadsign Ayuda's players run on Windows or Linux.
Static – Broadly, an ad or campaign that is presented on physical media. These may be signs or installations on vehicles.
Stretch – Stretch ensures that the digital design fills the space even if the aspect ratio for the screen or zone is different. The default is set to None.
- Fill – The recommended stretch setting. This setting is the most conservative and generally avoids sizing errors.
- None – The image is displayed at its native size. If the dimensions are smaller or different from the display area, black bars may result.
- Uniform – Expands the image until either the horizontal or vertical sides touch two sides of the display area. This may result in black bars.
- Uniform to Fill – Expands the image from the centre so that the design fills the display area. This may result in cropping.
- Custom – Set a custom width and height.
Sync Groups – Sync Groups allow two or more digital faces to operate in sync. The faces in the group use the same schedule, the same loop, spot transitions and same content played, and timing. The faces will present content in sync in all respects. The Sync Groups feature is often used with the Design Variations function.
T
Tags – Optional ad hoc labels that can be added and searched for later. Tags do not contribute to ordering or the management of content in any way.
Teams – Teams are a label for grouping users (see Also Linked Users, Roles, Types).
Title – Job titles associated with users. These have no impact on roles, teams, permissions or types of access.
Types – User Types describes what level of access the user has to business information (see also Linked Users, Roles).
Transit – An ad or campaign appearing on vehicles.
U
Unbooked Playback – A feature that allows digital filler to be displayed. Otherwise, the filler would need to be scheduled which rather defeats the purpose of filler.
Unsynchronized Bundles – Special bundles for instances when a follower player cannot play the file that its Leader player is ordering it to display. Left uncorrected, the follower player's loops would get out of sync. Instead, the follower player will play a spot from this unsynchronization bundle.
V
VAST – Video Ad Serving Template is a specification released by the Interactive Advertising Bureau (IAB) that sets a standard for communication requirements between ad servers and video players by using XML. With so many platforms, operating systems and device types, and the technological fact that serving video to players versus browsers is technologically different. VAST provides a common protocol. It does not matter where the ad is played, it will be understood if an ad should play, how should it be presented, how long it should last, if it can be skipped, where to find it, what it should click through to and other properties (see VPAID).
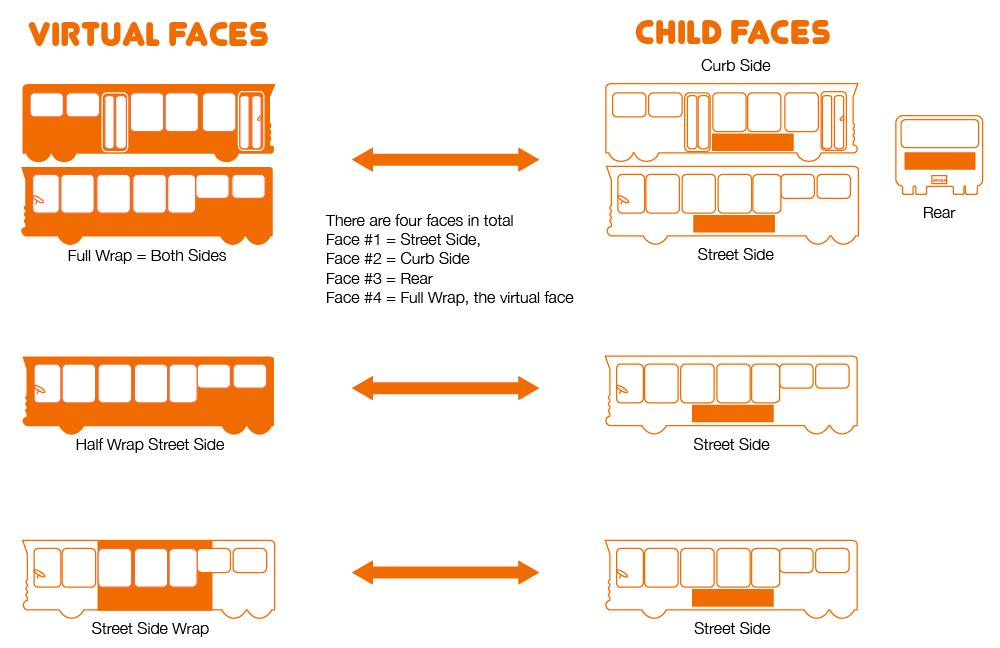
Virtual Face – Within Broadsign Ayuda faces can have subsets. The terminology differs for digital and static.
- Digital – A digital face might have two areas inside it, perhaps top and bottom. These are called zones.
- Static – On a bus with a face on either side and the rear, the entire bus is called a virtual face that groups three faces.
Transit OOH makes considerable use of virtual faces for vehicles.
Virtual faces, such as wraps on buses, are faces that envelope other faces. For example, full bus wraps are surfaces added to the exterior of buses that cover the sides and rear faces of the bus.
- The faces covering other faces are tracked independently as virtual faces.
- The child face is the face that is covered with the virtual face and therefore becomes unavailable when the virtual face is booked.
Void – The location was previously contracted but you want to keep it in the segment for informational purposes. The difference between Void and Delete is that the void option will display a red line and the fields will not be editable while the deleted booking line will not be visible once the delete option is selected.
If a Face has already played (or been posted) in a segment, or it has already been invoiced, the user cannot delete the segment, only void it.
VPAID – Video Player-Ad Interface Definition is a specification released by the Interactive Advertising Bureau (IAB) that sets a standard for communication interaction between ad units and video players. It enables interactivity and measuring of how well a video ad does through engagement tracking. Codes running within video players can add overlays and other features such as counting triggered responses. It also provides POP feedback so that stakeholders can be certain their ads are playing.
How does it differ from VAST? VPAID allows the tracking of individual ad performance. An example of a VPAID enabled interaction would be that a user could click an ad to view more detailed content such as a longer version of a pre-roll. Whatever action the user takes is recorded and reported back to the advertiser.
| VAST | VPAID |
|---|---|
| VAST is a universal specification for streaming video to compliant video players. | VPAID adds interactivity and playback features that are beyond the VAST spec. |
| It provides a uniform way for streaming video data to be passed from ad server to video players independent of the player hardware. | It facilitates complex behaviours, video players can accept more ads and offer more interactivity so that greater value is achieved for the consumer, the media owner and the buyer. |
| VAST does not support preloading video. | VPAID enables video players to preload content. |
| Simply, VAST is a common language for communicating with players. No matter how the ad is served – via DFP, DCM, or any ad server – the video player will understand and will display the content. | VPAID is a 'common language' to ensure communication between the video player and ad servers. |
Note: VPAID ads that are delivered via VAST tags are regularly referred to as VPAID tags.
W
Waitlisting – When a face is booked in one static proposal and then booked again in another static proposal a waitlist warning may be presented. The second face will be in a queue, in case the contracted contract gets its status changed to cancel.
Weekly Scheduler – The tool for organizing when digital content in a campaign will be shown on players.
Work Orders – These are what the operations manager uses to dispatch bill posters to put up static designs. In terms of Broadsign Ayuda, these are what links the postings to static faces. There are subtypes of work orders such as work orders such as work orders for filler, cover or copy changes as well as repairs and installations.
Z
Zones – See Virtual Face.