A rate card is where face prices are set.
Rate Card Types
There are four rate card types:
| Type | Description |
| Flat Rate Cards | Flat rates are constant prices. These will be used in most cases. |
| CPM Rate Cards | CPM Based rates allow users to enter Audience data, and have that data affect the pricing of their inventory. Cost per thousand (CPM) is a marketing term used to denote the price of one thousand advertisement impressions. |
| Audience-Based Rate Cards | Impressions and demographics are used to value the face. |
| Additional Revenue Rate Cards | Rates for other costs such as content creation, production, installation, fines and fees. This rate card exists in parallel to the other three. |
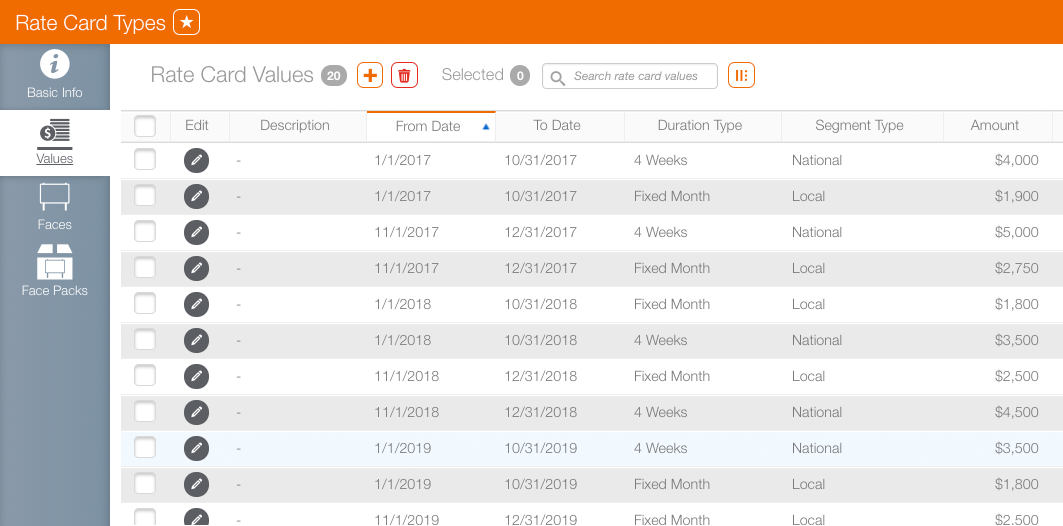
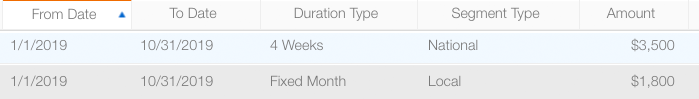
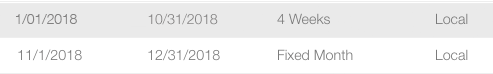
This table shows how rate cards have been configured for national and local campaigns, and for holiday as well as regular periods.
The result? It automatically calculates the billing amount.
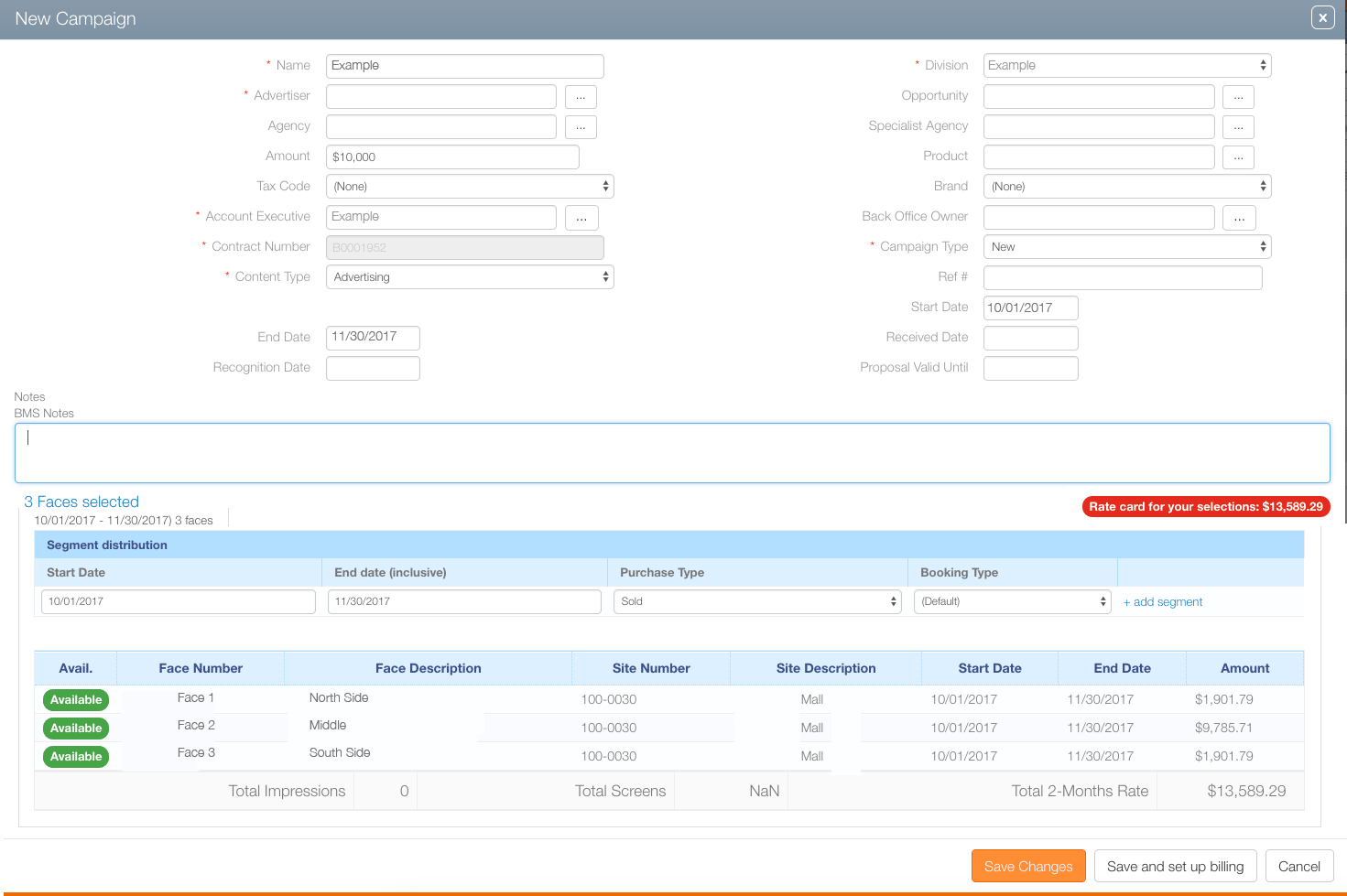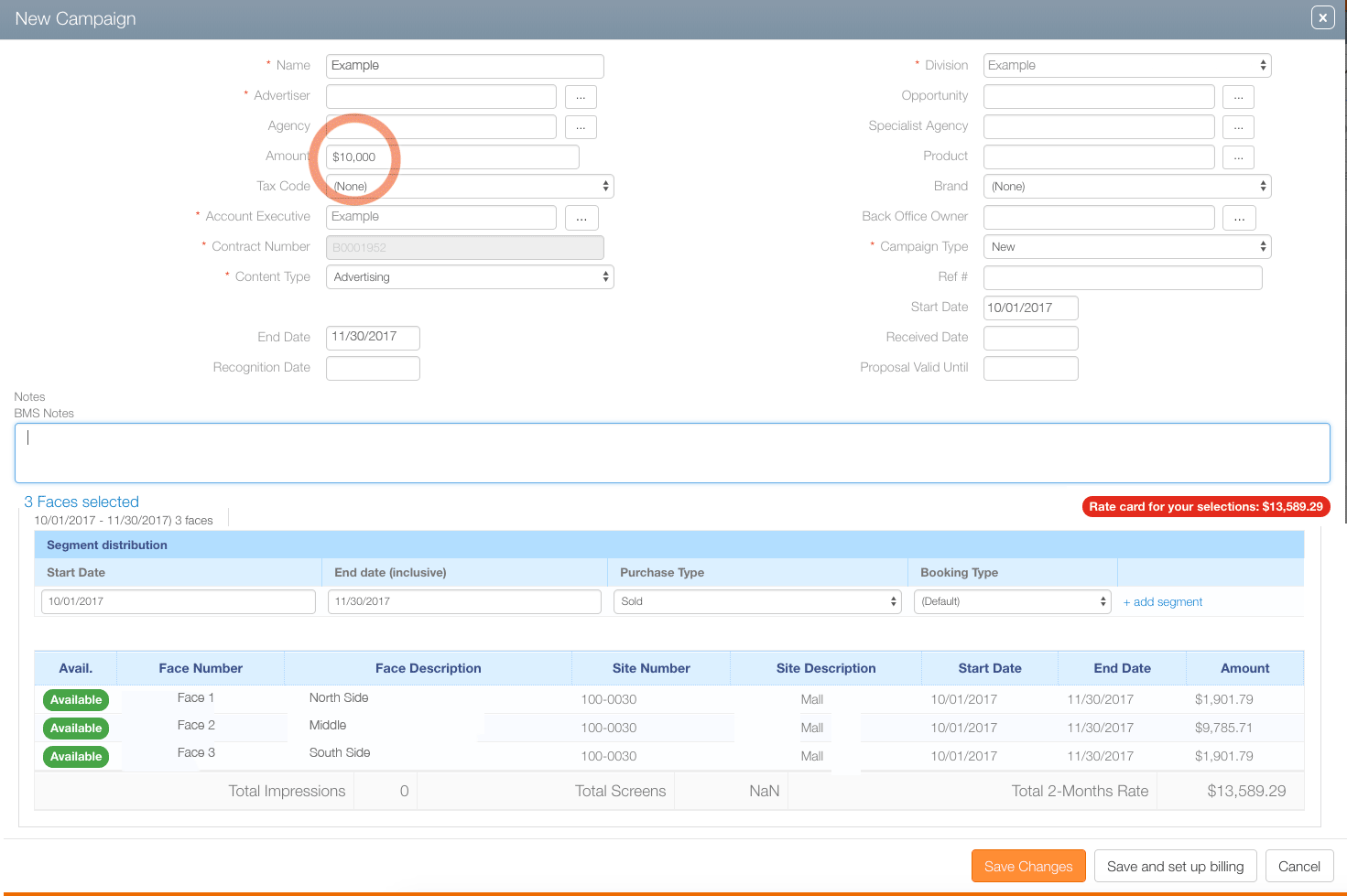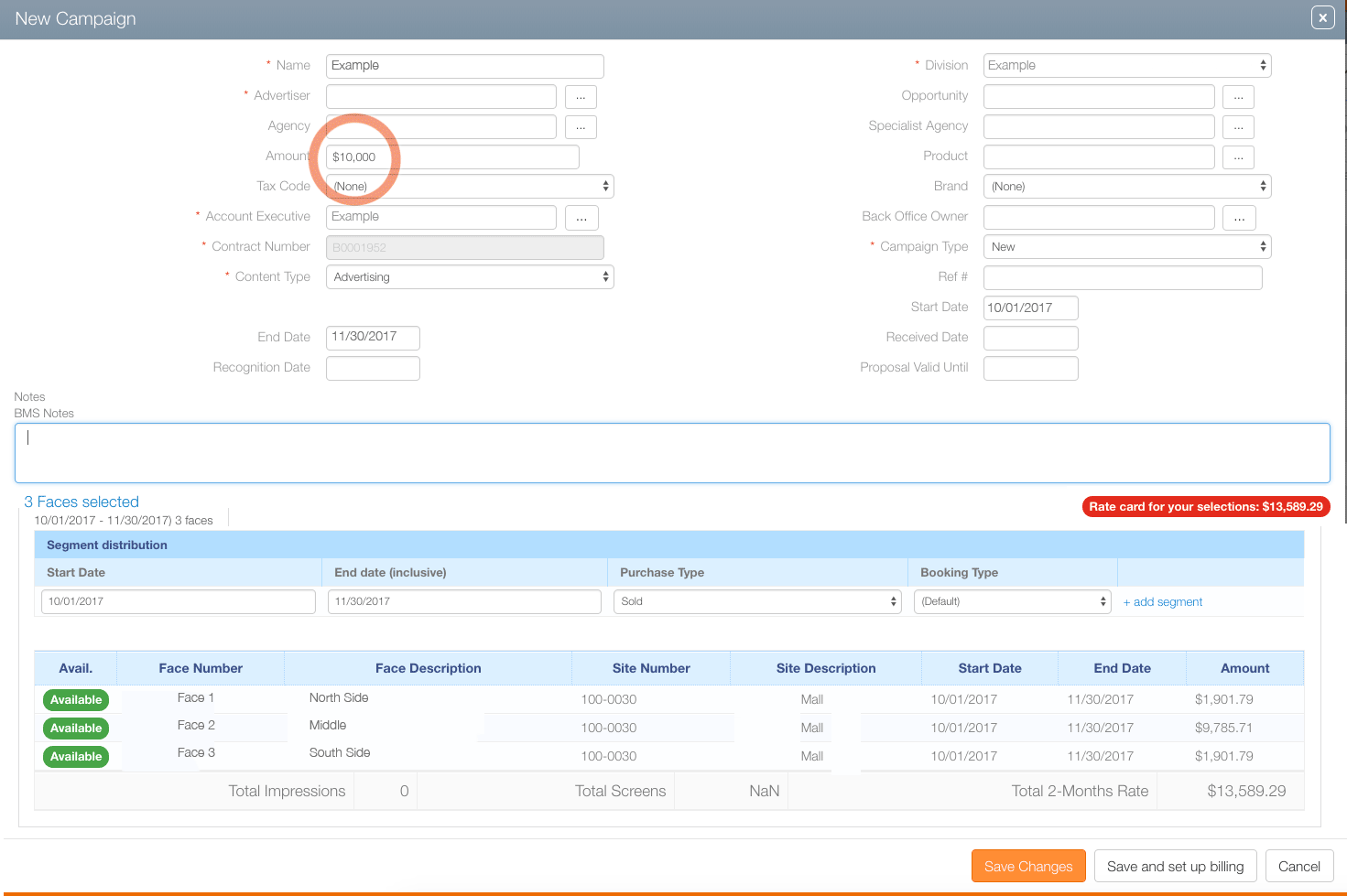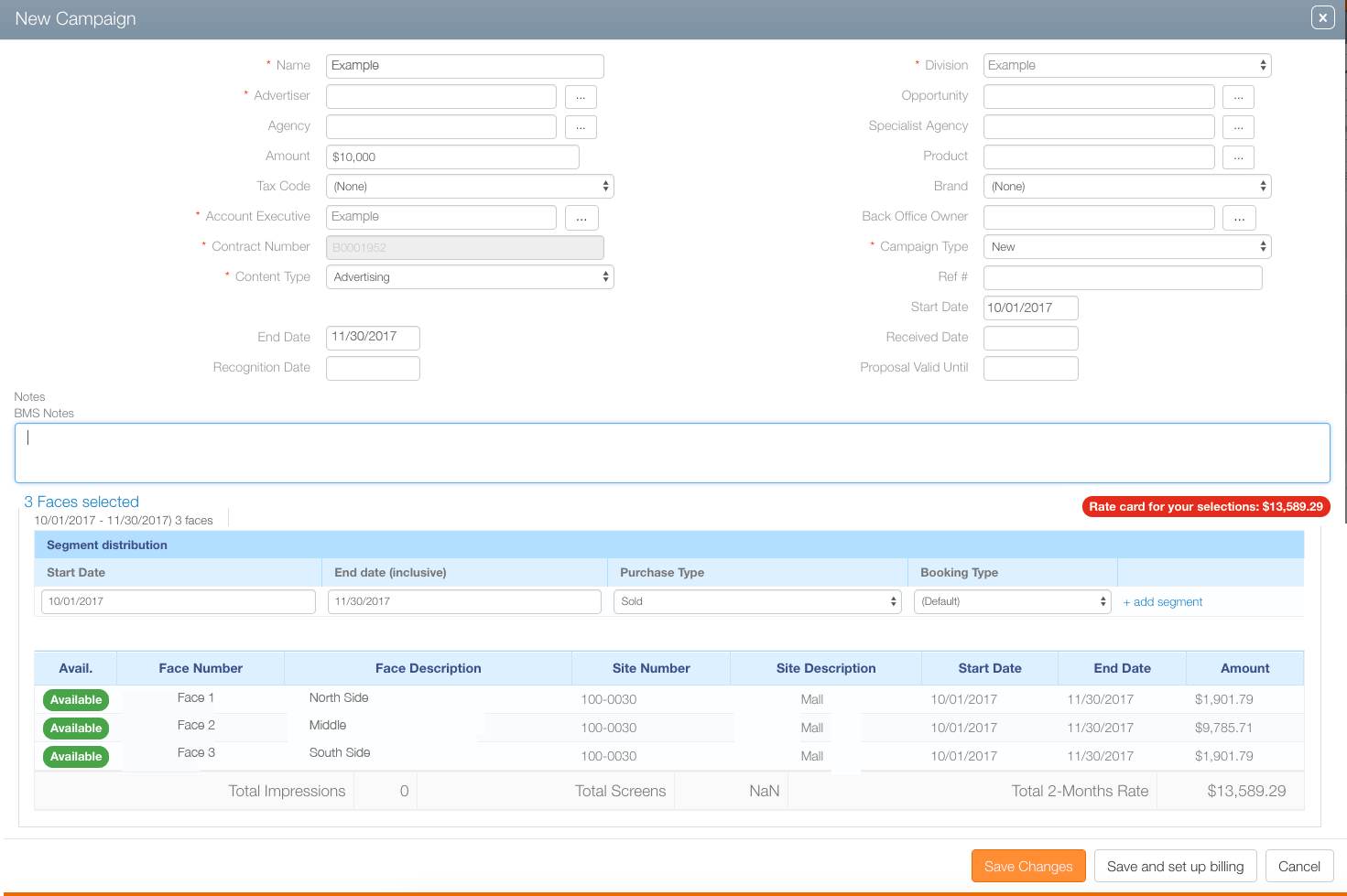
In this example, the sales user tried to enter $10,000 as the campaign total. However, the Rate card for your selections: $13,589.29 message appears in highlighted text. Because the enterd amount is less than the amount calculated by the rate card, manager approval will be needed to proceed with this lower price.
One, plus the additional revenues rate card. Meaning, all active rate cards linked to that face can potentially be used if a face is available for sale, however, only one applies for the proposal.
For example, there may be two rate cards available for national and local campaigns, and both apply to a face or face pack. Ultimately, only one will be used for the campaign.
The Additional Revenue rate card operates on top of this. Additional revenues can include fines, fees and business charges. Some additional revenues may even be face specific; for example, a roadside billboard may require two workers and a ladder truck. Because rate cards are linked to faces, the additional revenue rate card will come into play and have those installation fees added automatically.
The system calculates prices based on when rate cards are active. To use the example above: there are two rate cards, one for the regular season and one for the holidays. If a campaign spans both periods, Broadsign Ayuda automatically switches between rate cards and includes the correct prices using the different rate cards on the days when they are in effect.
Typically, advertising buyers will pay less than the price included in the rate card as they negotiate for discounts and the sales team offers incentives.
Rate Cards must be unique. Broadsign Ayuda prevents users from creating rate cards that have the same characteristics. This safety feature prevents the accidental creation of rate cards by different team members and the miscommunication that might result.